HTML canvas bezierCurveTo() Method
Example
Draw a cubic Bézier curve:
JavaScript:
var c = document.getElementById("myCanvas");
var ctx = c.getContext("2d");
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(20, 20);
ctx.bezierCurveTo(20, 100, 200, 100, 200, 20);
ctx.stroke();
Try it Yourself »
Browser Support
The numbers in the table specify the first browser version that fully supports the method.
| Method | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| bezierCurveTo() | 4.0 | 9.0 | 3.6 | 4.0 | 10.1 |
Definition and Usage
The bezierCurveTo() method adds a point to the current path by using the specified control points that represent a cubic Bézier curve.
A cubic bezier curve requires three points. The first two points are control points that are used in the cubic Bézier calculation and the last point is the ending point for the curve. The starting point for the curve is the last point in the current path. If a path does not exist, use the beginPath() and moveTo() methods to define a starting point.
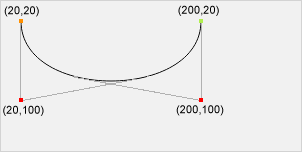
Start point
moveTo(20, 20)
Control point 1
bezierCurveTo(20, 100, 200, 100, 200, 20)
Control point 2
bezierCurveTo(20, 100, 200, 100, 200, 20)
End point
bezierCurveTo(20, 100, 200, 100, 200, 20)
Tip: Check out the quadraticCurveTo() method. It has one control point instead of two.
| JavaScript syntax: | context.bezierCurveTo(cp1x, cp1y, cp2x, cp2y, x, y); |
|---|
Parameter Values
| Parameter | Description | Play it |
|---|---|---|
| cp1x | The x-coordinate of the first Bézier control point | Play it » |
| cp1y | The y-coordinate of the first Bézier control point | Play it » |
| cp2x | The x-coordinate of the second Bézier control point | Play it » |
| cp2y | The y-coordinate of the second Bézier control point | Play it » |
| x | The x-coordinate of the ending point | Play it » |
| y | The y-coordinate of the ending point | Play it » |
